When we talk about binaural beats, or tones, or brainwave entrainment as a whole, we're simply taking about frequency, or frequencies. Unsurprisingly, most people don't really know what this means.
In this article we will simplify frequency-based music, so that you can get a good idea of how it works and what's really going on when you listen along.
What Is a Frequency?
Frequency refers to how fast an object vibrates. All sound is made up of frequencies, of vibrations. In fact Einstein famously said, “Everything in life is vibration”.
Frequency is measure in Hertz (Hz). We measure Hz as 1 kHz = 1000 Hz. This is the same concept as 1m = 100 cm.
In terms of sound frequencies, high frequencies are associated with treble. In music this will be the percussion and high notes of vocals and instruments such as the piano or guitar.
Low frequencies are associated with bass. In music this is the bass guitar and foot drum.
High sound frequencies have a fast wave pattern, and low frequencies have a slow wave pattern. This is an important part of the theory when creating brainwave entrainment music.
Generally speaking, the higher a frequency the more stimulating it is. Lower frequencies are slower and induce a more meditative state, while higher frequencies are faster and influence higher-energy brain activity.
Take for example a program designed for sleep. This would use a frequency below 4 Hz – slow and relaxing. Now consider a program designed for high-level focus. This would use a frequency above 12 Hz – faster, to keep the brain alert and engaged.
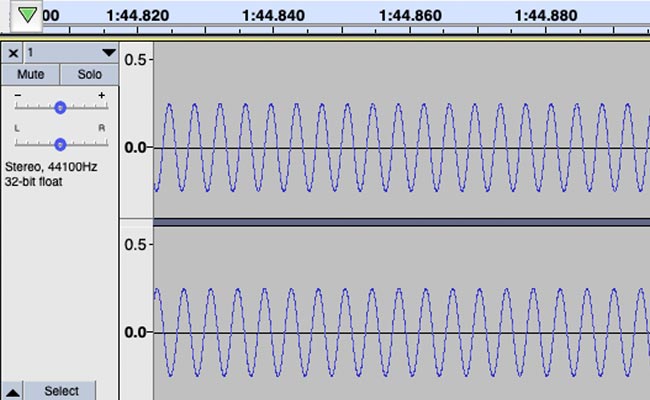
What Is Going On Underneath the Track?
All our programs contain pleasant, meditative music. Underneath that music is the frequency track, or binaural beats. We blend this in, harmonically, with the music, but if you listen carefully you will hear the frequency track humming along underneath the music.
It is simply a collection of vibrations, of sound frequencies, as demonstrated in the image above.
The not so simple part is that each frequency track (binaural beats) is created at a specific frequency – often more than one frequency – depending on the intended outcome of the program.
If you want to hear what a pure binaural beats frequency track (also known as a tone) sounds like, you can listen to the test sample here.
Furthermore, when you download one of our programs you will get a ‘raw tone' file in your download package. This raw tone is the frequency track on its own, containing no music overlay. You will notice that the higher the frequency the higher the tone, as we covered earlier on in the article.
For example, a 14 Hz Alpha binaural beats tone will sound higher in pitch than a 6 Hz tone (more treble). The latter will sound more bass-heavy.
How Is a Binaural Beats Frequency Made?
All music is made up of sound frequencies. For example, a piano chord (2 or more notes played together) contains multiple frequencies that span a frequency range. Some are lower, some are higher, and some will be in the mid-frequency range. It depends where you play the chord on the piano.
Binaural beats create a sound in the same way, although the sound lacks harmonics (multiple frequencies) because it is intentionally concentrated around one specific frequency at a time. This is why it sounds flat like a tone, without much variation in the sound.
So, you see, it is simply sound, albeit a concentrated sound of one particular frequency.
The more complicated understanding of how binaural beats are created is centered on the conversion of two frequencies (tones). I have linked to an article that will explain more on this at the end of this page.
The Power of Vibration and Frequency
When you consider that everything around us is comprised of energy (vibrations) it isn't hard to see how the brain is influenced by different frequencies.
Whether it is birdsong, the buzzing of a dragonfly's wings, or the wind blowing through the trees, everything has a frequency that affects us in a different way.
The amazing thing is that we don't need to be able to hear sound to be affected. The vibrations of sound can be felt. You can test this by placing your hand over a headphone cup or speaker woofer when music is playing. The vibration will penetrate through your body. As we have written about here, the deaf can also benefit from music healing through vibration.
Binaural beats music works by sending specific sound frequencies to the brain, which cause the brain to move into a specific state of consciousness. This means we can use sound to help us sleep, relax, focus, feel more positive, and even lower blood pressure or relieve a headache.
Again, we already know this to be true because music has been used for thousands of years to not just celebrate and bring us joy but also to relax and heal.
Hopefully this article has helped you connect the dots and understand exactly what these frequencies are playing under your binaural beats music. Now it's time to learn exactly how the science of binaural beats occurs inside your headphones and transmits to your brain.









